U.S. Economic and Market Highlights
The Economy:
- The European Central Bank and Bank of Canada reduced rates by 0.25% in June while the Federal Reserve held steady and suggested a rate reduction later in the year.
- Central Bank interest rate decisions are being made to balance inflationary pressures with slower economic growth trends in the next step in the process to unwind higher interest rates that were initiated over the last two years.
- The U.S. inflation rate fell to 3.3% in May. Core CPI, which strips out changes for food and energy prices, hit 3.4%, below expectations. This positive report boosted the stock and bond markets, as well as the U.S. Dollar compared to other currencies.
- GDP Growth rates around the world have been moderate and slowing due to higher interest rates, slower consumer spending, and higher geopolitical anxiety over conflict zones and this year’s elections. Global GDP growth is projected at 3.1% in 2024, with emerging markets expected to grow faster than developed markets.
- Existing home sales were at their lowest in 30 years last month because of higher mortgage rates. The pace of home price appreciation also slowed to what is estimated to be 3.8% in 2024.
- The U.S. and Eurozone leaders announced more tariffs on goods made in China to stimulate a diversification of supply chains to other countries for products such as industrial products (steel and aluminum), semiconductors, electric vehicles, solar cells, and medical products. Vietnam, Indonesia, and India are countries who will likely benefit from this supply chain diversification.
Fixed Income:
- Total returns from the bond markets were positive in May as long-term interest rates declined, helping to boost bond prices, and yields remained higher than average on shorter-term fixed income securities.
- The inverted yield curve reached its longest period on record of 20 months since short-term yields have exceeded longer-term yields. In the past, an inverted yield curve has been a reliable predictor of an economic recession, which triggers Central Banks to loosen monetary policy and lower short-term interest rates.
- Current interest rate sensitivity levels (see table below) show promise of compelling fixed income returns as markets anticipate lower interest rate scenarios over the next 12 months.

- With the bond market rally due to lower interest rate trends, investment inflows into fixed income investments is on the rise and the supply of new corporate bond issuance is up 21% versus 2023.
Equities:
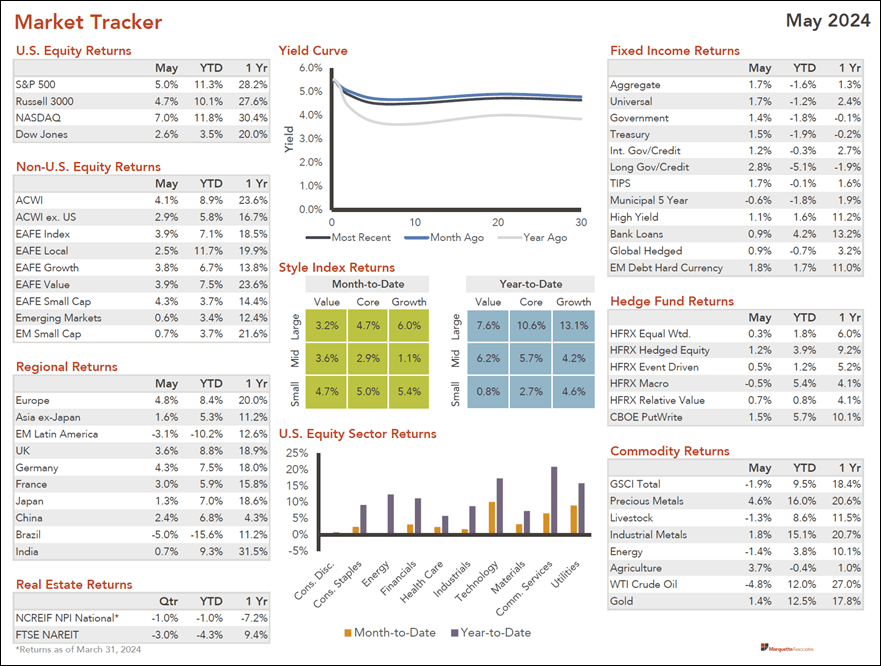
- A welcome rally in equities in all markets, except Brazil and Latin America, pushed some stock indices to all-time highs in May. The S&P 500 topped 5,400 for the first time and celebrated the 20-month anniversary of the bull-market as stock prices continued to rise during the period by more than 20%.
- U.S. Stocks are up nearly 13% this year followed by markets in Europe and Asia with high single-digit returns. Technology and communication services sectors continue to dominate the rest of the equities in the markets. (See the Market Tracker below.)
- Brazil and Latin American stock markets have lagged with double digit negative returns YTD. Higher interest rates have slowed the economy, lower currency values against the USD have increased import costs, declining commodity prices have reduced profits, and new government policies have concerned both local and foreign investors.
- Small-cap stocksare back in vogue with a powerful rally in May, as indicated by the Russell 2000 Index. The index gained 7.1%outperforming a rise of 4.5% for the large-cap index S&P 500. The outperformance came as investors flocked to cheap and undervalued segments of the market.
This communication was prepared for informational purposes only and is not an offer to buy or sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy or sell any security/instrument or to participate in any trading strategy. Past performance is not indicative of future results. See below reference sources used in preparing the above information.

